Table of Contents
Abdominal pains are widespread symptoms. Doctors usually divide the abdomen into four quadrants due to the number of organs and structures found to arrive at a timely diagnosis and treatment. The right upper quadrant (RUQ) is below the right rib cage.
Pain in this area can be caused by multiple pathologies that affect organs such as muscles, the liver, the gallbladder, the right kidney, and the rib cage. This article will discover an extensive list of other causes and practical relief solutions.
Why is muscle pain on the right side under the ribs?
To unravel the origin of discomfort beneath your right ribcage, let’s explore the organs in this region. The upper right quadrant houses crucial organs, including (1):
- Abdominal muscles
- The gallbladder
- A section of the liver
- The right kidney
- The small intestine
- The large intestine
- The pancreas
The pain intensity in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) can fluctuate based on the underlying condition, ranging from a persistent ache to a sudden, sharp stabbing sensation. RUQ pain may arise from any of the organs situated in this region.
What are the possible causes?
Abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant may be due to several causes, from minor problems, such as trauma to the area, muscle strains, or costochondritis, to more serious problems affecting the organs in that region, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, right kidney, small intestine, and colon.
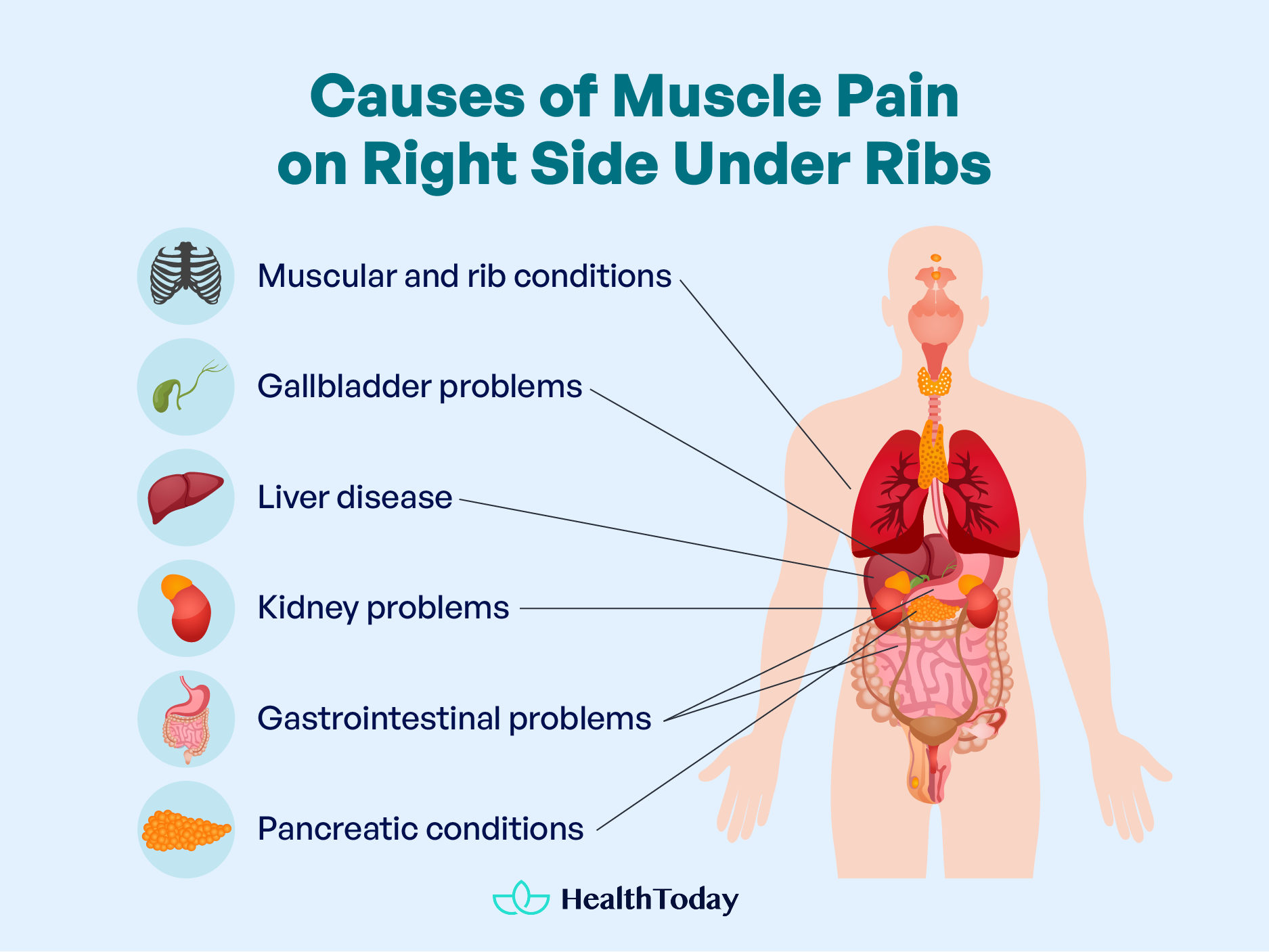
Muscular and rib conditions
Pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, caused by muscle and rib problems, can originate from various conditions. Intercostal muscle injuries or muscle strains can trigger discomfort following vigorous physical activity.
Likewise, rib problems such as fractures or inflammation of the rib joints resulting from trauma can contribute to pain in this area.
Symptoms of muscle or rib problems are usually pain that increases in intensity with movement and subsides with rest (2). In rib lesions, the above symptoms are mainly added to the stabbing pain localized at a specific point, which is exacerbated by breathing. To determine the appropriate treatment, it’s crucial to identify the underlying cause through medical evaluation to determine the appropriate treatment.
Gallbladder problems
The primary cause of right upper quadrant pain is gallbladder inflammation or cholecystitis.
Cholecystitis is often triggered by a blockage in the main opening of the gallbladder, resulting from either a gallstone or biliary sludge. When gallstones advance through the duct, they may stop in the bile duct, initiating a cascade of inflammation (4), known as choledocholithiasis, which can cause right upper quadrant pain (RUQ).
Pain in the RUQ due to gallstones is characterized by colicky pain, which appears after a large meal, may radiate to the back, and usually lasts several hours. It is essential to be attentive to accompanying symptoms, which may include (3):
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Chills
- Dark urine or pale stools
- Yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
If you experience symptoms related to gallstones or choledocholithiasis, you should visit a doctor or go to the emergency room. Gallstones in the bile ducts can cause serious complications that require immediate attention.
Liver disease
Liver diseases are a range of conditions that affect the normal functioning of the liver. Different conditions such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, liver abscess, or liver cancer can also cause pain in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) (5).
Symptoms of liver disease may include:
- Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Leg and ankle swelling
- Itchy skin
- Chronic fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Easy bruising
- unexplained weight loss
You should seek medical attention if you experience pain in the right upper quadrant, along with symptoms that are consistent with a liver condition.
Kidney problems
One of the causes of RUQ pain is renal disease, which affects the right kidney. These diseases can be infectious, inflammatory, obstructive, or tumorous. If the cause is severe, over time, it can lead to kidney damage or kidney failure. In terms of frequency, we have the infectious and obstructive causes much less frequent than the inflammatory and tumor ones.
- Upper urinary tract infections (or pyelonephritis): Are among the most common causes of abdominal pain. They are caused by bacteria that travel up to the urinary tract or reach the kidney through the bloodstream. Symptoms may include abdominal pain radiating to the back or side, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, cloudy or bloody urine, and painful urination (6).
- Obstructive causes include kidney stones: These are caused by the formation of solid deposits of minerals and salts in the kidney or in the ureter, the tube that carries urine to the bladder. Stones can block the flow of urine and cause severe pain in the ureter that moves into the groin, nausea, vomiting, bloody or foul-smelling urine, and urinary urgency or frequency (7).
If you’re experiencing right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain related to a kidney issue, you’re advised to book an appointment with a healthcare professional or visit an urgent care center.
Gastrointestinal problems
Several gastrointestinal issues can lead to right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain, include:
- Indigestion: Also known as an upset stomach, indigestion results in abdominal discomfort.
- Gastritis: This condition involves inflammation of the stomach lining, often caused by infection caused by Helicobacter pylori.
- Peptic ulcers: These sores develop on the stomach lining, known as gastric ulcers. .
The pain associated with these conditions typically presents as a dull, burning sensation. Other symptoms may include an uncomfortable feeling of fullness, abdominal bloating, burping or gas, nausea, and vomiting.
These conditions are usually treated first with a healthy diet, avoiding irritants such as spicy foods, alcohol, and coffee, and increasing water intake (8). Your doctor may prescribe a stomach protector and a diet change if the discomfort persists.
Pancreatic conditions
Pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas that occurs less frequently than cholelithiasis, urinary tract infections, and renal lithiasis (9).
- Causes: It has several causes, such as gallstones, alcoholism, certain medications, elevated triglyceride levels, and pancreatic cancer.
- Symptoms: Typical clinical symptoms are upper abdominal pain, back pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and fatty stools.
- Treatments: Treatment strategies depend on the severity and underlying cause of the disease. It can range from medical treatment to avoiding irritants such as alcohol and fatty foods or surgical treatment if more severe.
- Complications: Possible complications are serious and include kidney failure, respiratory problems, infections, bleeding, abscesses, and sepsis.
If you experience these symptoms, you should consult a physician for appropriate evaluation and treatment.
Conditions related to pain on the right side under the ribs
In addition to the conditions mentioned earlier, right upper quadrant pain can also be triggered by the following underlying conditions:
- Right lung base pneumonia
- Herpes zoster
- Electrolyte disturbances such as hypocalcemia or hypokalemia
- Dehydration
- Hiatal hernia
They are much less frequent but should be considered a differential diagnosis of the above causes.
When should I get medical help?
Right upper quadrant pain can indicate various health conditions, including severe medical conditions.

Specific symptoms may indicate a medical emergency. You need immediate medical attention if you have:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Fever
- Persistent nausea and vomiting
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal swelling or tenderness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
If pain persists for a few days, talk to your doctor to determine the cause and the best treatment.
While some causes of right upper quadrant pain can resolve naturally, other causes can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Preventions and treatments for muscle spasms under the right rib
Management and prevention of right upper quadrant abdominal pain hinge on its underlying cause.
For muscle spasms induced by vigorous physical activity or trauma-related pain, the recommended approach involves physical rest and the use of analgesics like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or diclofenac to alleviate symptoms. Concurrently, proper rest, hydration, and a balanced diet form the foundation for effective rehabilitation.
In the case of prevalent causes like biliary diseases (e.g., cholecystitis or biliary colic), preventive measures entail (10):
- Avoid fatty and fried foods: They can trigger the formation of gallstones, which can obstruct the gallbladder and cause pain.
- Moderating alcohol intake: Alcohol can affect the composition of bile, contributing to the formation of gallstones. It is recommended to reduce its consumption.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise: A healthy lifestyle, including regular physical exercise, helps maintain a stable weight, controlling cholesterol levels, and therefore preventing the formation of gallstones.
- Maintaining adequate hydration: Good hydration prevents excessive concentration of salts and minerals in the bile, reducing the risk of stone formation. Two liters of water per day is recommended.
Consultation with a doctor is necessary when abdominal pain arises. They will perform an ultrasound for a precise diagnosis. Treatment options vary, ranging from non-surgical interventions, often involving antispasmodics, to surgical procedures when warranted. Caution against self-medication is emphasized to prevent masking symptoms and complicating the condition.
Preventive measures for infectious causes like pyelonephritis include:
- Sufficient water intake: Drinking enough water is essential to prevent urinary tract infections. Water dilutes urine, which helps to reduce substances that may favor bacterial growth. In addition, the act of urinating cleanses the urinary tract by flushing.
- Proper genital hygiene: Good genital hygiene can help prevent urinary tract infections. Wipe the genital area from front to back after using the toilet to avoid transferring bacteria from the anal area to the urethra. It is also recommended to urinate after sexual intercourse to prevent bacteria from moving up the urethra.
- Try not to hold back the urge to urinate: It is expected to avoid often going to the bathroom because it is not the time or place. These acts allow microorganisms to enter the urethra and cause urinary tract infections.
Prompt consultation with a doctor is crucial upon infection, involving a urine test and likely antibiotic prescription.
Gastrointestinal causes such as gastroesophageal reflux, gastritis, or gastric ulcers prompt medical intervention. Doctors may prescribe medications like proton pump inhibitors or antacids to alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Surgical causes, such as choledocholithiasis, large renal lithiasis, or tumor-related issues, often necessitate surgical procedures as the primary course of action.
How do you know if your side pain is internal or muscular?
It can be challenging to differentiate between internal pain and muscle pain, but several factors can help understand it. Muscle pain usually presents as localized discomfort affected by movement and related to recent physical activity. Pain usually worsens on palpation and becomes apparent as a dull ache.
In contrast, internal pain may be deeper, less localized, and associated with organ-specific symptoms such as nausea or changes in bowel habits. It may not be significantly affected by exercise and may be persistent or occur suddenly and intensely.
Is it kidney pain or muscle pain?
Pain produced by the kidneys, as opposed to muscular pain, is usually colic, mainly localized in the lumbar area, and radiates to the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, usually accompanied by urinary symptoms.
What are the 3 symptoms of a muscle strain?
Muscle strains, characterized by stretching or tearing muscle fibers, present distinctive symptoms. The affected area is characterized by sudden, localized pain accompanied by swelling, bruising, and tenderness.
Why is my muscle pain not going away?
Chronic muscle pain after an injury can have multiple causes. Inadequate rest, incomplete healing, and early repetitive strain can hinder recovery. To achieve lasting relief from persistent muscle pain, it is essential to visit a physician for a thorough evaluation and proper rehabilitation.
Can muscle pain take months to heal?
Muscle pain after an injury can vary from a few days to months, depending on the severity, such as whether the muscle injury also involves tendons or bone avulsions. To end the pain effectively, you should consult a physician to determine the severity of the injury.
Summary
Many pathologies cause muscle pain on the right side under the ribs, related to many organs in this area, including muscles, the liver, the gallbladder, the right kidney, and the rib cage. While some causes of right upper quadrant pain can resolve naturally, other causes can lead to severe complications if left untreated, which need immediate medical attention. The prevention and treatments for right upper quadrant abdominal pain depend on its underlying causes. Treatment options vary, ranging from non-surgical interventions, often involving antispasmodics, to surgical procedures. It’s always suggested that you should consult with your doctor when abdominal pain arises.
















Comments
0