Table of Contents
Coconut sugar is a natural extract obtained from the sweetened sap of the coconut tree. It is prepared by cutting a small part of a coconut flower to obtain the sap. Coconut sugar is a better alternative and is used as a sweetener for coffee, chocolates, tea, and bread.
It can taste like a bit of brown sugar with a tint of caramel flavor and appear differently depending on the source and time of harvesting. Is the sweetener backed by scientific research? Is coconut sugar healthy for you? We have got you covered. This article will provide an honest and unbiased review of the glycemic index, research backing, benefits, side effects, and other things to help users make informed decisions.
What is coconut sugar?
This sweetened extract contains 70 to 79 percent sucrose and 3 to 9 percent glucose and fructose, respectively (1). It has long been routinely used in places like Indonesia and the Philippines. It is prepared by heating the sap of coconut palm flowers for more than 3 to 4 hours until it becomes thick.
Many people get confused between coconut and palm sugar in Asian markets. But these two are quite different. Coconut sugar originates from coconut palm trees, whereas palm sugar is obtained from different palm trees. It is rich in B vitamins and minerals like iron, magnesium, zinc, and potassium.
How is coconut sugar made?
It is made in five steps that are as follows:
1. Collecting the coconut sap
The trees with unopened flower clusters are chosen for collecting the sap. The flower is kept in a bent position for about a week to stimulate the flow of the sap. The clusters are tied and pulled carefully, and a 6mm cut is made in sap. The sap is collected and stored in a plastic container, and it is allowed to be cooked for 5 hours. Then, the cooked sap is evaluated for quality based on pH (more than 6), level of sweetness (13-14.5), color (beige to light brown), and translucent clarity.
2. Water removal
Boil the collected sap in a stainless steel container until it reaches up to 115°C. When it starts boiling, skim away the foam to prevent dark residue formation. Boil the sap for 3 to 4 hours to remove excess water. The exact time for boiling will vary depending on the cooking method and the quantity of sap.
3. Transferring the sap
When brought to a boil, the sap should be continuously stirred to prevent burning. Remove it from the heat as the sap turns viscous and difficult to boil. Keep stirring at room temperature to turn it into granules.
4. Drying
Allow the mixture to cool down, and press it to break the clumps. A sieve makes the granules in uniform shape and size for good quality. Dry it on a stainless steel tray over boiling water for 1 hour to reduce moisture. Once it becomes dry, let it cool before use.
5. Packaging
Transfer the cooled mixture into a large container and let it rest overnight. Afterward, the coconut sweetener is weighed and packaged into transparent plastic bags for commercial distribution (2).

What does coconut sugar taste like?
This substance’s taste can vary depending on the method used for processing and brand. Some products taste more like caramel or have a slightly bitter flavor. It has a rich and complex taste that is quite different from regular white sugar. Many people say that it has an earthy taste with a tint of maple flavor. Hence, it is used as a natural sweetener.
The health benefits of coconut sugar
Prevent Decrease in Glucose Levels
It works similarly to brown and cane sugar by increasing blood glucose levels to prevent the occurrence of hypoglycemia (3).
Reduces Blood Glucose Spikes
This additive contains inulin, a fiber that is soluble in water. It prevents sudden rises in blood glucose levels after meals, making it a better option for diabetic individuals (4).
Nutrition facts
One teaspoon has the same number of calories as white and cane sugar. Here’s the nutritional profile:


Coconut sugar contains small amounts of vitamins and minerals, including Vitamins C and E, Zinc, Potassium, Iron, and Phosphorus. It also contains antioxidants such as polyphenols and flavonoids (5). However, it is important to remember that it is still a sugar in spite of these properties.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index (GI) measures how carbohydrate-containing food affects your blood glucose levels, rating them on a scale from 1-100 (5). Higher numbers indicate a faster rise in blood glucose levels. Individuals managing diabetes find the glycemic index valuable for monitoring blood glucose levels. It has a glycemic index of 35. The table below provides a comparative analysis that will help to determine the overall healthiness.
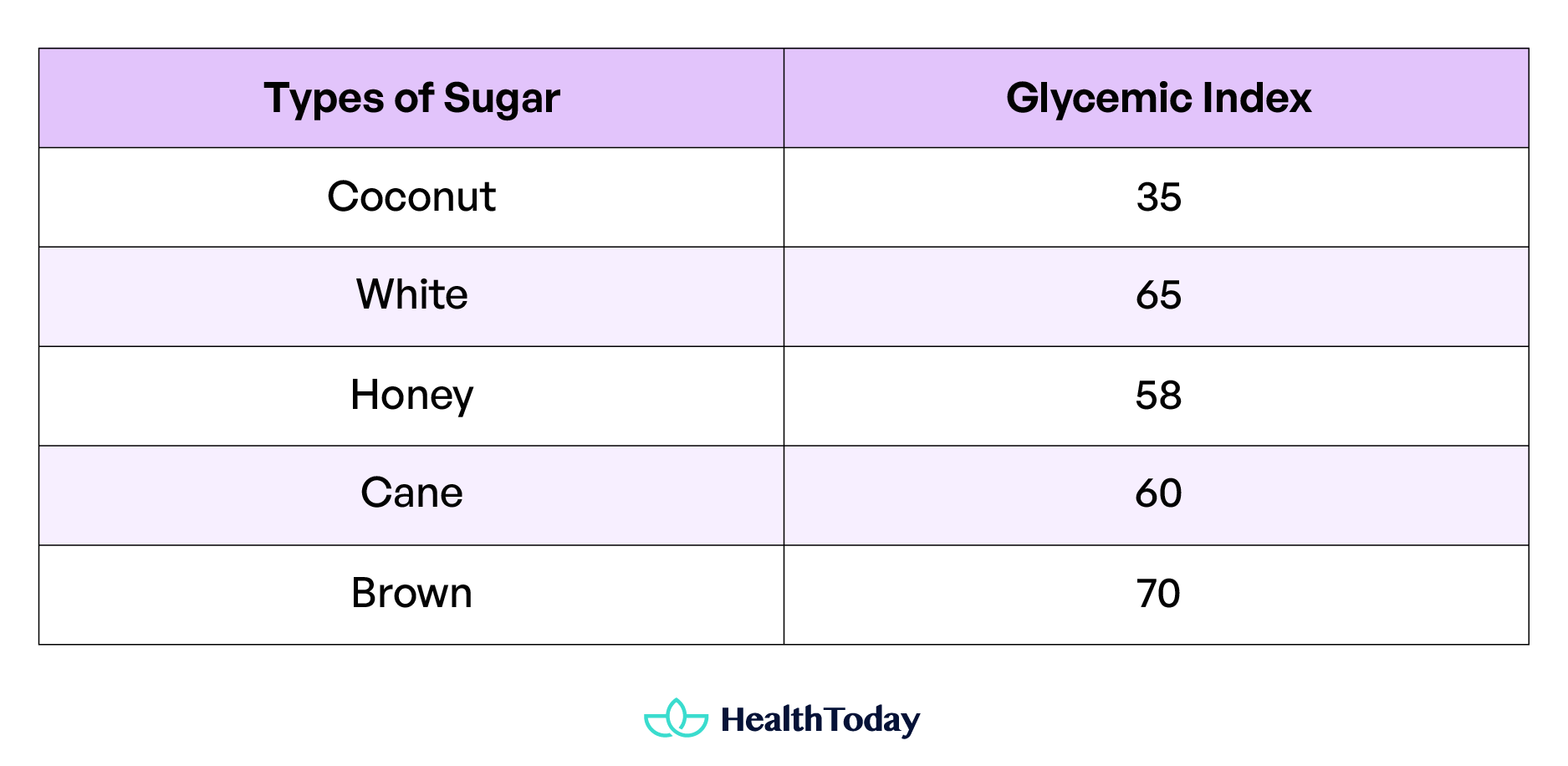

It has a lower glycemic index compared to other sweeteners. The low glycemic index is attributed to several factors, including inulin, which slows down absorption and maintains blood glucose levels, composition, and the method used for processing (6).
Can diabetics eat coconut sugar?
Overeating can increase blood glucose levels, thus posing health risks. To avoid this, some individuals experiment with various sweeteners. One of the popular choices is a sweet extract obtained from coconut for those managing diabetes. However, is this substitute a safer option? Despite its lower glycemic index than the traditional additives, it remains rich in carbohydrates, ultimately increasing glucose levels.
Is coconut sugar good for weight loss?
This sweetener is high in calories (1 teaspoon = 16 calories) and carbohydrates. So, it is not a good fit for weight loss. If you consume 100 grams, you’re taking 100 grams of carbohydrates with 75 grams, totaling around 375 calories.
Here’s the tabular explanation of the calorie content of both products:
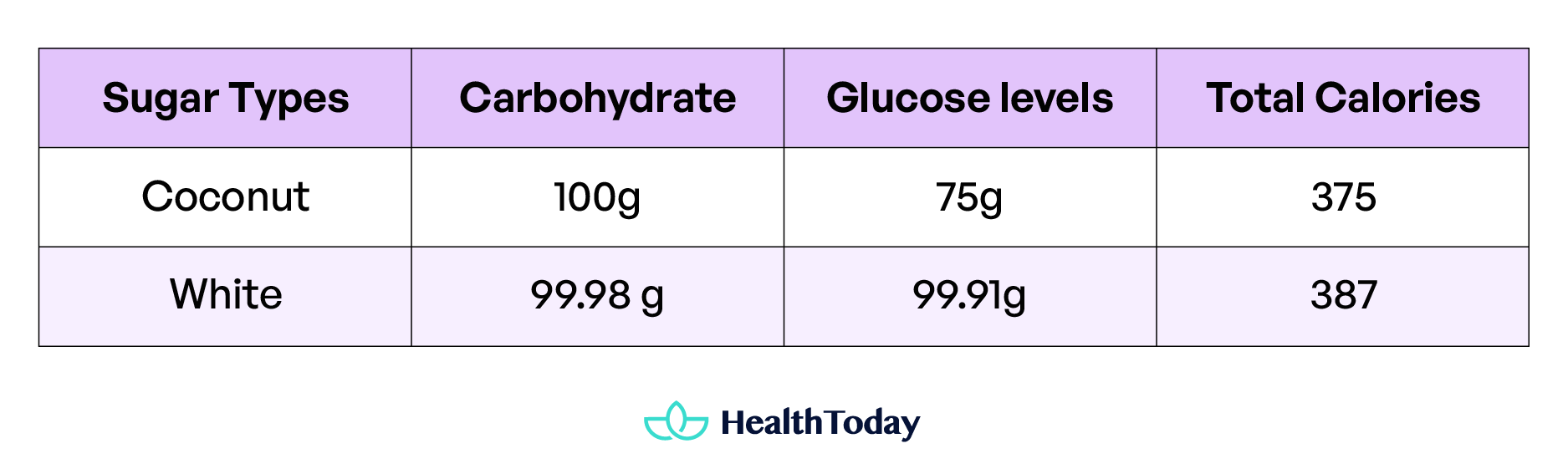

Experts recommend that women limit daily sweetener intake to no more than 6 teaspoons. Men should aim for 9 teaspoons regardless of whether it’s a processed product or naturally derived from coconut (7).
What is coconut palm sugar?
It is an organic sweetener created by collecting the sap from palm flowers. Usually, the sap is collected overnight and harvested from the tree in the morning. Then, the sap is boiled with water until it evaporates at 160° C to form sticky crystals.
Often referred to as unrefined, this product undergoes minimal processing and is devoid of chemical additives. Sourced from a variety of palm trees, including date, toddy, palmyra, nipa, and coconut palms, it offers a natural sweetening option.
What does coconut palm sugar taste like?
It is known for its molasses-like flavor and caramel texture, enhancing recipes with a richer taste compared to conventional cane sweeteners.
Is coconut palm sugar healthy?
While coconut palm sweeteners present some minor distractions from conventional sweeteners, they aren’t notably healthier. They boast a slightly lower glycemic index, potentially resulting in a milder increase in blood glucose levels. Additionally, they contain low amounts of nutrients like iron, zinc, and potassium (8).
However, these amounts are so small that you would need to consume large quantities to gain any nutritional benefit. Despite its minimal processing compared to refined white sweeteners, coconut palm still contains high levels of calories and sweetening agents, akin to conventional alternatives. Therefore, it’s important to consume in moderation.
How different is coconut palm sugar vs coconut sugar?
Coconut palm sugar and palm sugar are derived from the sap of their respective palm trees. However, the latter originates from a distinct palm tree variety, contributing to its unique flavor profile. Despite these disparities, both can be seamlessly substituted in recipes without concern for the final result.
Why is coconut sugar better than other sugars?
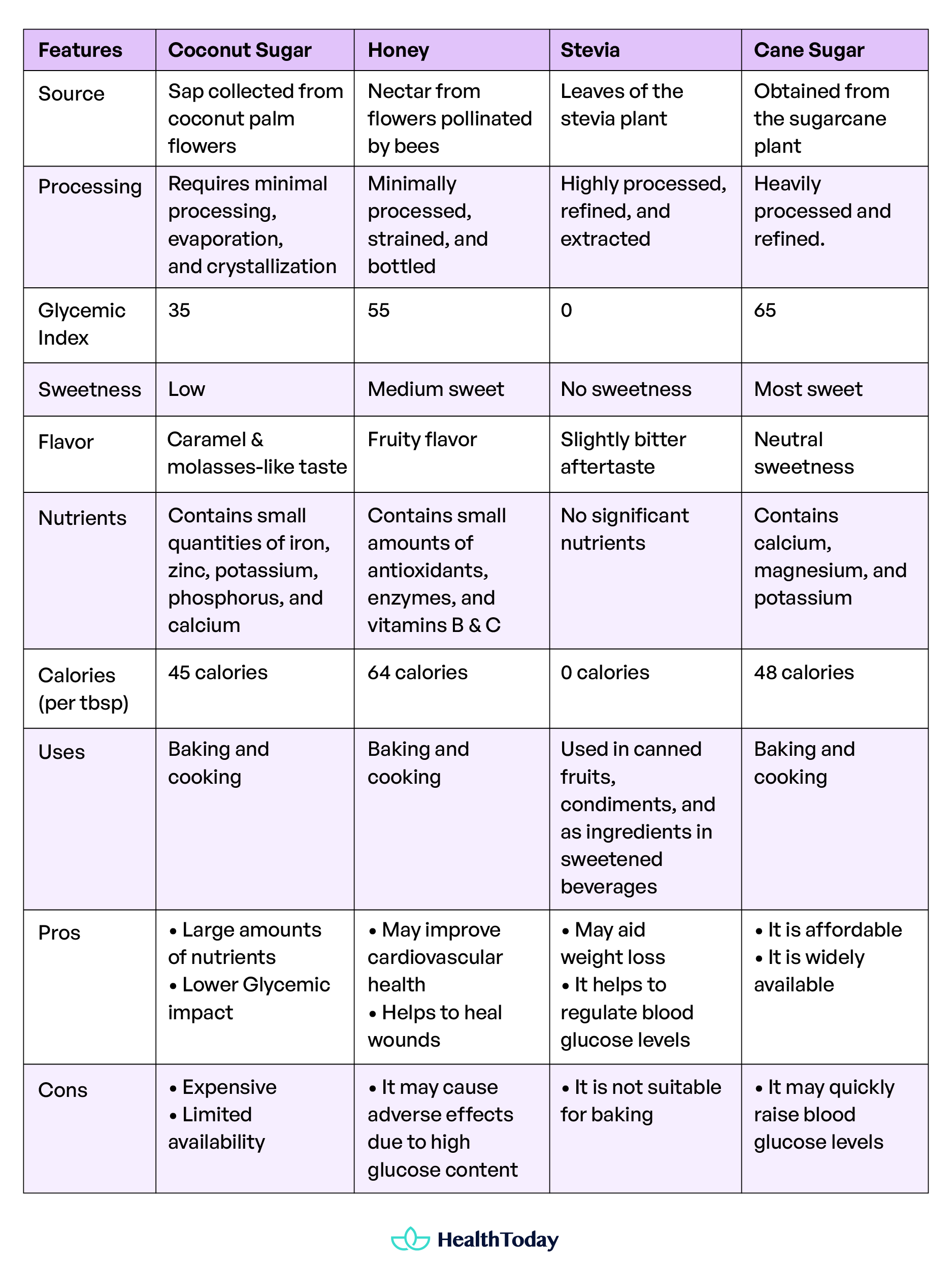

Coconut sugar studied possible effects
Increase blood glucose levels
Even though it has lower levels of fructose than regular additives, it can still increase blood glucose levels and reduce insulin sensitivity (9).
May contribute to weight gain
It contains huge amounts of carbohydrates that can contribute to weight gain. Individuals aiming to lose weight should consume in moderation (10).
May impede metabolism
While small amounts of coconut-derived sweeteners may support a healthy metabolism, excessive intake can have the opposite effect.




Coconut sugar substitutions
Maple sugar
This sweetener is obtained by dehydrating the liquid maple syrup, leaving behind granules (11). They look quite similar because they both are light brown in color. It usually tastes like maple syrup but doesn’t have the caramel-like flavor of coconut-derived sweetener. It is used in a 1:1 ratio as a substitute for coconut sweetener.
Turbinado sugar
It is a partly-refined extract that keeps some of the molasses, giving it a slightly caramel taste. This natural substitute is called raw, given its minimal processing. It exhibits a coarse texture and is insoluble than other refined sweetening agents. So, it is an excellent replacement when you grind it into a fine powder (12).
Date sugar
It is created by grinding dates into a powder. Due to its high fiber and minerals, it is commonly considered a healthier alternative in recipes (13). It is used in a ratio of 1:1 as a substitute.
Palm sugar
Some people confuse this sweetener with coconut palm-derived alternatives, but it is sourced from palm trees such as date, nipa, or palm. It is similar to coconut sweetener in terms of processing method, taste, and texture, making it an excellent substitute that can be used in quantities similar to coconut sugar (14).
Brown sugar
This substitute is mixed with molasses giving it a stronger and sweeter taste than plain white sweetener and can be used in a 1:1 ratio (15).
Sucanat
It is less processed than others. It is golden in color and tastes like caramel, which makes it a good alternative. Its coarse grains don’t allow it to dissolve easily, so it can be sprinkled on food or ground into a fine powder while cooking (16).
Panela sugar
Panella is shaped like a cone. It is named Piloncillo in Mexico and Jaggery in Asian countries (17). It undergoes less processing than conventional sweetening agents and shares a taste profile similar to that of brown alternatives.




How to choose coconut sugar?
The best choice is organic, unrefined coconut sweet extract. Some individuals mistakenly purchase brown alternatives, assuming they are coconut palm-derived, but that’s not accurate. While coconut palm sweeteners may appear similar to other alternatives, they originate from distinct trees and may occasionally contain added white sweetening agents, which is not considered healthy.
To ensure quality and safety, look for packages labeled as 100 percent pure without any other additives or fillers. It is important to buy from a reliable store, either online or in person.
How to store coconut sugar?
Keep this sweetener fresh by packaging it in a sealed container in a cool, dry spot. Remember to close the container tightly after each use to prevent contamination. Proper storage can help maintain freshness for about two years. Your attention to such details ensures the quality and safety of the product for your enjoyment.
Is coconut sugar refined sugar?
This product is natural and not heavily processed. It adds much sweetness compared to a lot of other options.
Is coconut sugar good for keto?
It is incompatible with the keto diet, as just two teaspoons contain 8 grams of carbohydrates. For someone following a keto diet, which typically limits daily carbohydrate intake to around 50 grams, that’s about 16 percent of your total daily carbohydrates. So, using this sweetening agent isn’t practical if you’re trying to stick to your keto goals.
Is coconut sugar considered Paleo?
Daily intake in small amounts is okay if you’re following a Paleo diet because it is a natural sweetener with some good nutrients, unlike heavily processed additives.
Is coconut sugar gut-friendly?
This additive contains fibrous inulin, which is good for your gut. Inulin keeps gut bacteria healthy and might lower the chance of getting colon cancer (18).
Summary
Coconut sugar is a natural substitute for synthetic sweeteners, derived from the sap of coconut palm trees. Despite its popularity, limited scientific research supports its health benefits.
This sweetener has a low glycemic index compared to others, which makes it a good alternative. However, keep a purity check and understand its nutritional content for informed dietary choices. Due to its carbohydrate content, moderation is key, making it important to store it properly for optimal benefits.















Comments
0