Table of Contents
Can stress cause chest pain? Yes, it certainly can.
In fact, recurrent chest pain due to anxiety is one of the most common reasons people seek emergency medical services (1).
But how can you tell that the pain in your chest is triggered by stress? How do you know if it isn’t a heart-related issue? This blog post will help you distinguish between the two and offer four exercises to alleviate stress-induced chest pain.
Stress-induced chest pain: How does it feel like?
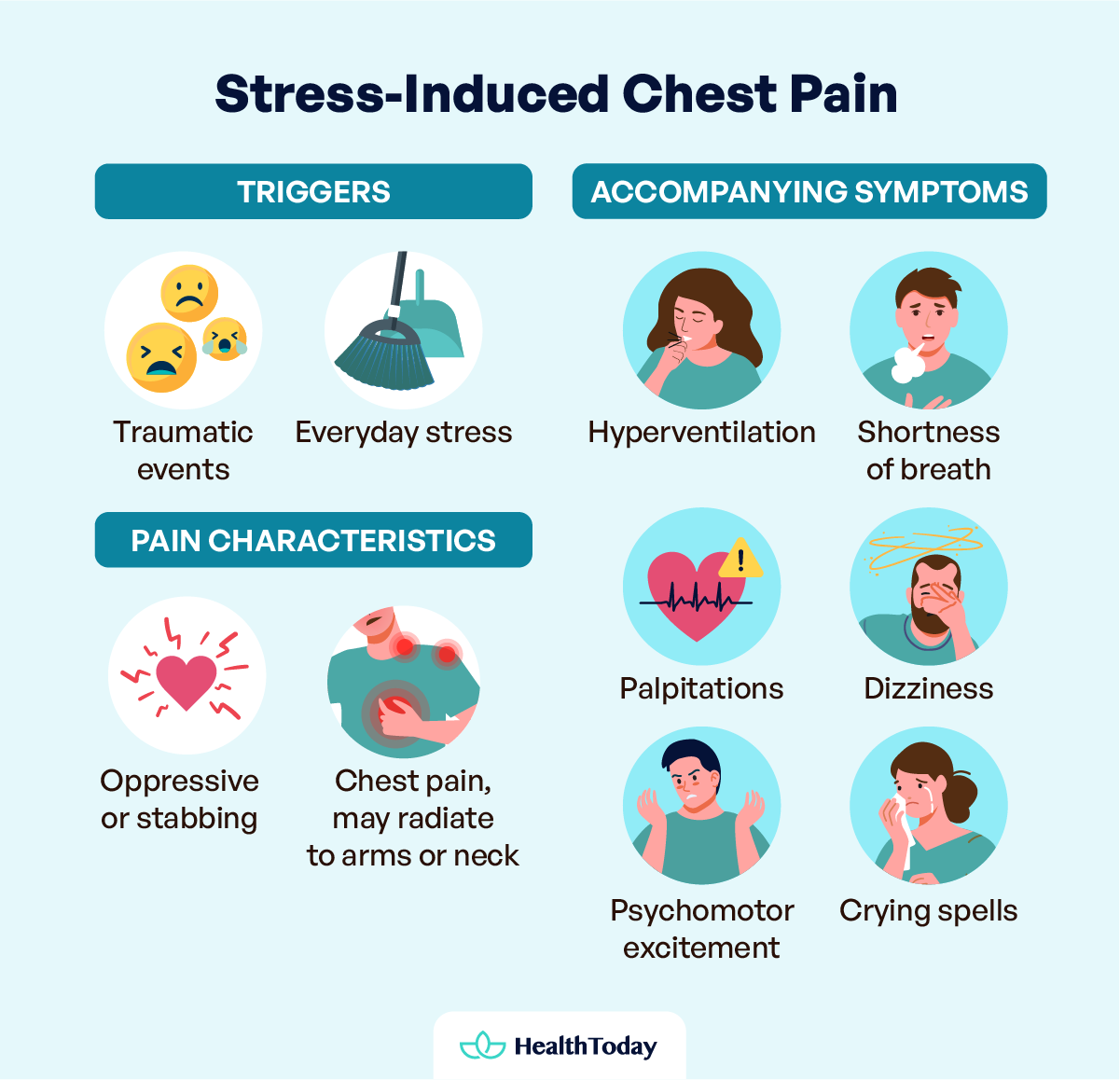
We usually have baseline anxiety that allows us to carry out daily activities without problems, but the question remains: can stress cause chest pain? When this anxiety caused by stress becomes uncontrollable, various symptoms may appear, such as chest pain. This is a common reason for emergency consultations (2).
The typical characteristics are:
- Trigger: Situations that can alter a patient’s emotions, acting as triggers, are common. These can include traumatic events, such as the death of a family member, as well as ordinary occurrences, like feeling overwhelmed by household chores.
- Type of pain: The type of pain can vary from oppressive to stabbing. It is usually localized in the chest, although it may radiate to either arm or neck in some patients.
- Accompanying symptoms: Hyperventilation, shortness of breath, psychomotor excitement, crying spells, palpitations, and dizziness are expected.
The symptoms can be confused with other much more serious causes of chest pain, such as angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. When in doubt, we recommend that you consult your doctor.
Anxious feeling in the chest or heart-related issues?

Chest pain is a very worrying and distressing symptom because cardiovascular diseases are usually present in the same way. Knowing the differences allows one to have better control of the situation and, at the same time, to clear doubts about the ailment. The differences are usually based on:
Background
Patients with cardiovascular diseases are usually sedentary, elderly, overweight, and smokers who often suffer from diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia (4). Heart disease is more frequent in men (5).
A traumatic situation, negative or accelerated thoughts, usually precedes anxiety. Anxiety is more frequent in women.
However, chronic anxiety is a risk factor for future cardiovascular disease, so the two could be related (6).
Symptoms
Anxiety may include tightness, pressure, constriction, or pain in the chest. Other symptoms can accompany it, such as palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or excessive sweating. The pain is often recurrent.
Cardiac problems, such as angina pectoris or heart attack, can also incite chest pain or discomfort. Angina pectoris is characterized by a squeezing pain in the chest that is usually triggered by physical exertion and improves with rest or medication (7). On the other hand, a heart attack involves a sudden blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle. It can exhibit oppressive chest pain that may radiate to the left arm, neck, or jaw, accompanied by symptoms such as sweating, nausea, and shortness of breath (8).
It is important to note that while anxiety can cause intense physical symptoms, anxiety-related chest pain is usually benign and poses no immediate threat to health. However, because of the similarity of symptoms, it is critical to rule out any underlying cardiac problems.
Why do I feel anxiety in my chest? Possible causes
The emotional factors that trigger chest pain are usually diverse and vary from person to person. They are often characterized by significantly impacting an individual’s life, who may feel overwhelmed and unprepared to cope.
The feeling of anxiety in the chest can have several underlying factors. First, it can trigger physical sensations in the chest, as stress and emotional tension can manifest in the body in various ways. Additionally, anxiety can cause hyperventilation, leading to a feeling of shortness of breath that exacerbates the pain.
During episodes of anxiety, the nervous system is excessively activated, resulting in palpitations, sweating, and chest tightness.
In patients with previous cardiovascular disease, it can be a trigger for angina pectoris, so it is important to rule out cardiac problems when symptoms occur.
Can panic attacks cause chest pain?
Panic attacks are sudden instances of intense fear or discomfort that peak within minutes. These attacks can cause mental symptoms, such as the feeling of imminent death, and intense physical symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, sweating, and tremors. Although very distressing, it is vital to remember that they don’t represent an imminent threat to life.
It is essential to differentiate a panic attack from the symptoms of a heart attack as they share similarities. If there is any doubt about the nature of the symptoms, it is advisable to seek emergency medical attention to rule out serious heart problems.
How to relieve chest pain from stress: 4 effective exercises

The demands of modern life have negative consequences on mental health, such as stress and anxiety. Therefore, physical exercise is a potent natural relaxant for both body and mind. It aims to reduce tension and alleviate the severity of negative effects by increasing the production of endorphins and serotonin. These neurotransmitters help regulate mood and make us feel good.
High-intensity workouts
According to a study conducted by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, published in 2022 in the Journal of Affective Disorders (9), frequent physical activity, including strenuous exercise, alleviates anxiety, even in chronic cases. High-intensity training possibly stimulates a greater release of endorphins and modifies brain chemistry more dramatically than lower-intensity workouts.
Outdoor walking: low-intensity exercise and change of scenery
Low-intensity exercises are just as beneficial for relieving anxiety and stress as high-intensity exercises. People can change their environment and focus on their surroundings to further “free” the mind.
German scientists conducted a study and published it in their journal called Molecular Psychiatry (10). They discovered that a one-hour walk in nature reduces stress. “Amygdala activation decreases after walking in nature, whereas it remains stable in an urban environment,” the experts stated in the document.
These results suggest that walking in nature positively influences health. It affects brain regions related to stress, thus improving the quality of life.
Dance
Dancing is a physical activity that can provide many benefits for those suffering from anxiety and depression. These benefits include endorphin release, stress reduction, increased self-esteem, and opportunity for socialization and emotional expression.
Numerous studies have explored how dancing affects patients with anxiety and depression, revealing a significant improvement in symptoms when individuals engage in the activity for 150 minutes weekly (11).
Yoga
Yoga is known for its many benefits to a person’s overall health. This activity incorporates a way for the “physical,” “mental,” and “spiritual” to unite.
Its performance has positive impacts on relieving symptoms of stress and anxiety. A systematic review found that yoga can reduce symptoms of depression in people with mental disorders. It was noted that the effectiveness increases with the frequency of weekly yoga sessions (12).
This activity is strongly recommended to improve quality of life and general well-being.
It is important to note that any of the above activities should be performed consistently, as beneficial results may take days or weeks to be noticed.
When to see a doctor
When experiencing chest pain caused by anxiety, it’s essential to know when to seek medical attention. While anxiety-induced chest pain is often benign, it’s crucial to rule out any serious underlying conditions.
- Severe or prolonged pain: If the chest pain is severe, persistent, or worsening over time, it’s urgent to seek medical help promptly.
- New or unexplained symptoms: If you experience chest pain along with symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, nausea, sweating, or pain radiating to the arm, jaw, or back, seek immediate medical attention.
- History of heart disease: If you have a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, or other cardiovascular risk factors, any chest pain should be evaluated by a doctor.
- First episode: If this is the first time you’ve experienced chest pain, it’s wise to get a medical assessment to determine the cause and rule out any serious conditions.
- Impact on daily activities: If the chest pain interferes with your ability to perform daily activities or causes significant distress, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Remember, it’s always better to err on the side of caution when dealing with chest pain. Seeking timely medical evaluation can provide peace of mind and ensure appropriate management of underlying issues.

Can you have chronic chest pain from anxiety?
Chronic chest pain or Recurrent chest pain can result from anxiety, especially in individuals with anxiety disorders. Recognizing the symptoms is essential so you know when to consult a physician.
Should I use medication for chest tightness from anxiety?
If you cannot control the symptoms of anxiety, your doctor will likely prescribe medication to improve your quality of life. These medications may include antidepressants and benzodiazepines, among the best known.
How to stop chest pain after a panic attack?
To alleviate chest pain after a panic attack, try deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and engaging in calming activities such as mindfulness or meditation. It’s also significant to address any underlying anxiety through therapy, lifestyle changes, and, if necessary, medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Can stress and anxiety cause sternum pain?
Stress and anxiety can be indicated by sternum pain due to increased muscle tension and changes in breathing patterns. This pain may feel like pressure, tightness, or discomfort in the chest area.
Summary
When experiencing chest pain due to anxiety, it’s crucial to differentiate it from heart-related issues and know when to seek medical attention. Anxiety-induced chest pain often presents as pressure, tightness, or discomfort in the chest area, accompanied by symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and sweating. Understanding the triggers and symptoms of anxiety-related chest pain can help individuals manage their condition effectively and reduce fear and anguish.
To relieve chest pain caused by stress and anxiety, physical exercises such as high-intensity workouts, outdoor walks, dancing, and yoga can be beneficial. These activities help reduce stress levels, release endorphins, and promote relaxation, contributing to overall well-being.
However, medical attention is essential if chest pain is severe, persistent, or is associated with other symptoms like dizziness, nausea, or difficulty breathing. Individuals with a history of heart disease or other cardiovascular risk factors should also consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate management.













Comments
0